

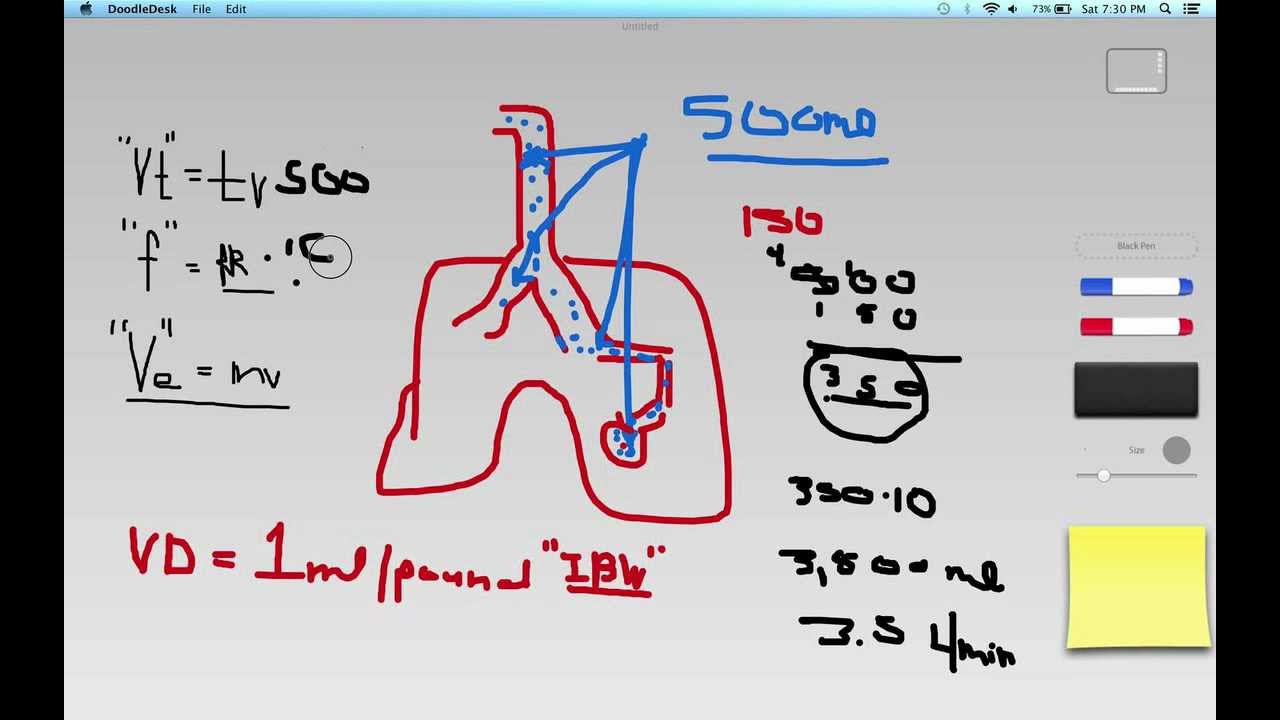
This includes what many authors would refer to as “ARDS mimics” as well as “true ARDS.” For the purposes of this chapter, ARDS will refer to the clinical syndrome as defined by the Berlin Definition (including a diversity of histological patterns – which in clinical practice is generally unknown).Many authors describe patients meeting the Berlin definition of ARDS who don't have diffuse alveolar damage as “ARDS mimics” (with the concept that only diseases causing diffuse alveolar damage are “true” ARDS).As discussed further below, patients should be optimized on the ventilator for >12 hours prior to proning, in order to sort out patients with pseudoARDS. PseudoARDS is clinically important to recognize because these patients generally respond well to high mean airway pressure, but do not benefit from interventions such as paralysis or proning.Acute onset (new or worsening respiratory symptoms within 300 mm (40 kPa) so patients no longer meet diagnostic criteria for ARDS.Start early enteral nutrition (even if proned and/or paralyzed).īerlin definition requires four criteria ( 22797452).Indicated if PaO2/FiO2 Consider after >12 hours of optimization on ventilator.Propofol and opioid will reduce respiratory drive and improve ventilator synchrony (but avoid prolonged high-dose exposure to these agents).Consider IV bicarbonate to increase the bicarbonate to ~30-35 mM (if needed to achieve adequate pH without lung-injurious ventilation).Consider if PaO2/FiO2 ~7.2 (unless elevated ICP or RV failure).
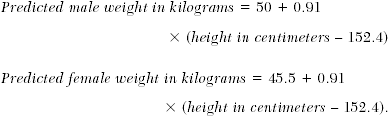
🔑 Often the most important intervention!.Intubated ARDS patient: therapeutic package ✅ investigate & treat underlying cause ( more)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
